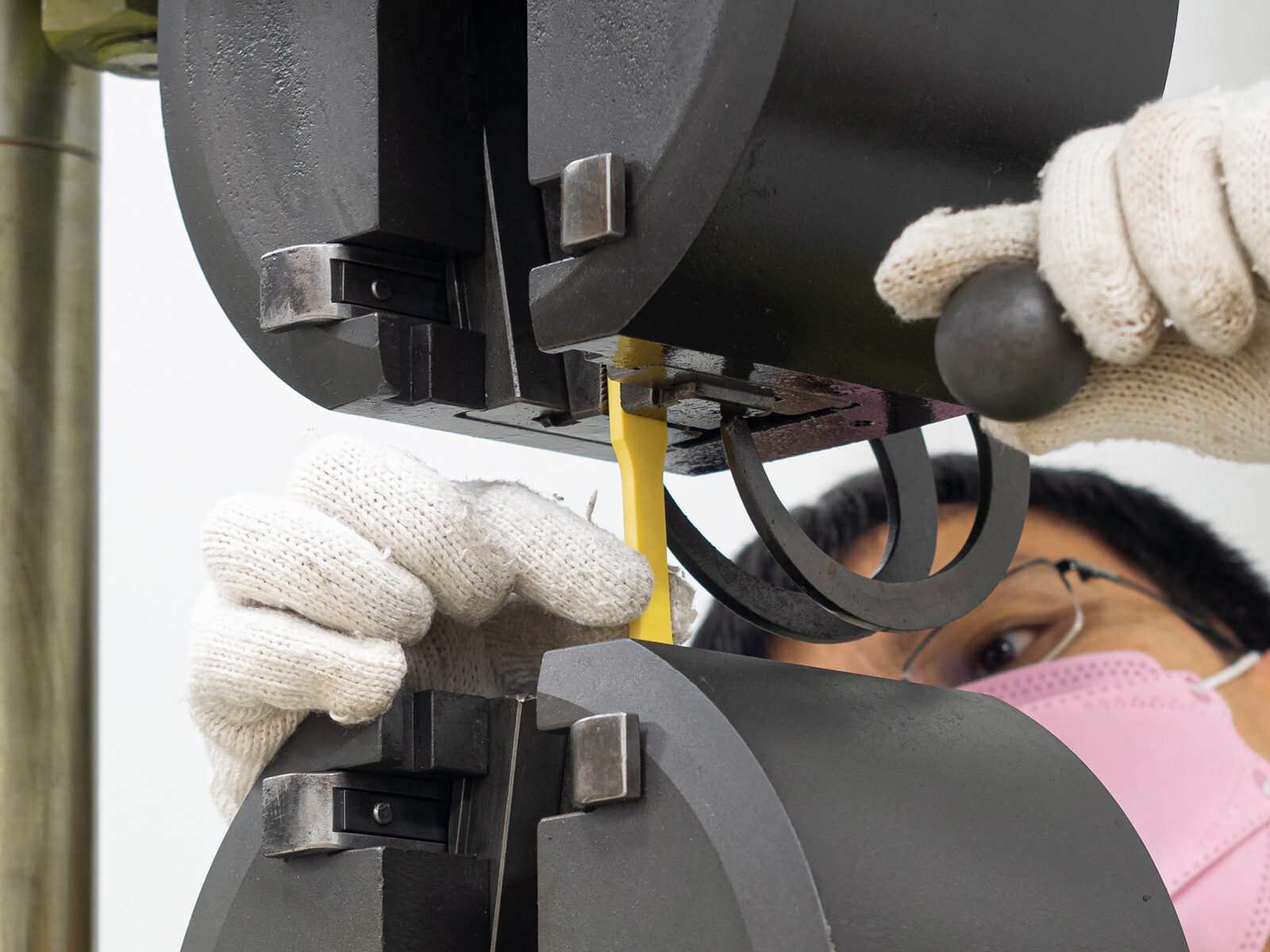
Applied Technical Services’ state-of-the-art metallurgy lab conducts plastic tensile testing, material identification, litigation support, and other metallurgical services. We employ lab professionals with decades of combined experience in mechanical and metallurgical industries.
What is Plastic Tensile Testing, and Why is it Important?
Plastic tensile tests measure a plastic’s ability to stretch before breaking and the load required to break the plastic. Tensile tests allow manufacturers to evaluate the quality and safety of materials. The benefits and advantages of tensile testing include:
- Quality Control
- Encourages Consistency in Manufacturing Process
- Ensures Compliance with Industry Standards and Regulations
Plastics are popular materials amongst manufacturers, so plastics must perform as intended in various applications. Tensile tests allow manufacturers to make informed decisions on the ideal uses of plastic materials, ensuring that the materials can withstand the physical demands of the applications.
ASTM D638
ASTM D638 is the American Society for Testing Materials’ standard specification for the tensile testing of reinforced and nonreinforced plastics. The test calculates the following mechanical properties.
Tensile Strength
Tensile strength is the amount of stress a material can endure before stretching or breaking. A material’s tensile strength heavily affects its potential applications. For example, manufacturers will avoid using brittle materials for structural applications because the materials lack the necessary properties. The following factors affect tensile strength.
- Composition and Molecular Structure
- The Material’s Temperature
- Measurement Errors
Tensile Modulus
Tensile modulus measures a plastic’s stiffness and predicts how the material will deform under significant loads. A material’s tensile modulus is affected by multiple factors, including:
- Composition and Molecular Structure
- Mechanical and Physical Properties that Influence Stress or Strain
- The Size and Shape of the Affected Area
- The Material’s Temperature
Tensile Strain
A tensile strain occurs when tensile stress causes deformation or elongation in a material. Tensile strain represents a ratio comparing an object’s extended length to its original length.
Elongation and Percent Elongation at Yield
Elongation at yield represents the ratio between the initial length of a specimen and its increased length after stretching or deformation.
Elongation and Percent Elongation at Break
Elongation at break represents the amount of deformation and stretching a material can endure before breaking. Materials with a higher elongation at break presentation are more ductile and thus more likely to deform without breaking.
The Applications of Plastic Tensile Testing
Multiple industries use tensile testing to evaluate the quality of plastic materials, including:
- Aerospace
- Automotive
- Construction
- Healthcare
- Manufacturing
- Pulp and Paper
Applied Technical Services’ Plastic Metallurgy Lab
Applied Technical Services provides quality engineering consulting, inspection, and testing services. Founded in 1967, our ever-growing list of clients spans dozens of industries worldwide. We are an ISO 9001:2015 registered management system that prioritizes customer service, continuous growth, and professionalism. We employ professionals of diverse backgrounds and disciplines and offer free quotes for our competitively priced services. Call +1 (888) 287-5227 and ask about our plastic tensile testing services today!