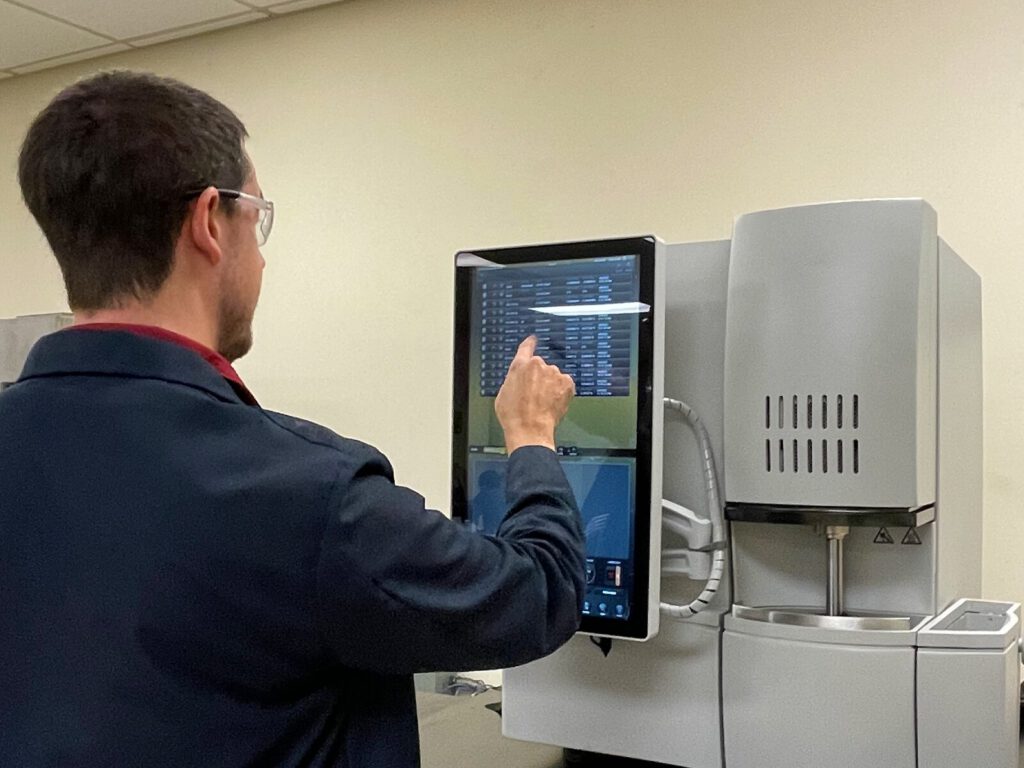
ATS generally uses a LECO Combustion instrument to analyze carbon and sulfur content in small steel samples that do not meet the size constraints of Optical Emission Spectroscopy (OES analysis).
How Combustion Testing Works
Combustion testing is a technique used to precisely determine the content of carbon, sulfur, nitrogen, oxygen, and hydrogen in metals and alloys. Fundamentally, this process involves burning the sample to release these specific elements. The values received for element percentages are matched against specifications to determine the metal type. ATS frequently performs this analysis on steel samples in addition to iron, nickel, titanium, and cobalt alloys.
Commonly Tested Analytes
- Steels and Cast Irons
- Reactive Materials
- Refractories
- Non-Ferrous Alloys
- Carbides
- Carbon
- Sulfur
- Nitrogen
- Oxygen
- Hydrogen
LECO Testing Standards
With several LECO combustion units in our facilities, ATS is equipped to provide quick and efficient elemental analysis to clients across industries. Our chemists regularly perform this testing in accordance with the following standards:
- ASTM E1019
- ASTM E1409
- ASTM E1447
- ASTM E1941
- ASTM E2575
About Us
ATS’s quality assurance program meets the most stringent industry requirements, including NQA-1 of the nuclear industry. We are an ISO 9001:2015-registered company with several ISO/IEC 17025:2017-accredited labs.
Contact Us
Click here to submit a request online or call +1 (888) 287-5227 to speak with a representative about your needs.